What is Hashimoto's?
Overview
Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck below the Adam's apple. The thyroid produces hormones that regulate many of the body's functions.
In autoimmune disorders like Hashimoto's disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. In this case, immune cells target and destroy the thyroid's hormone-producing cells, leading to reduced hormone production, known as hypothyroidism.
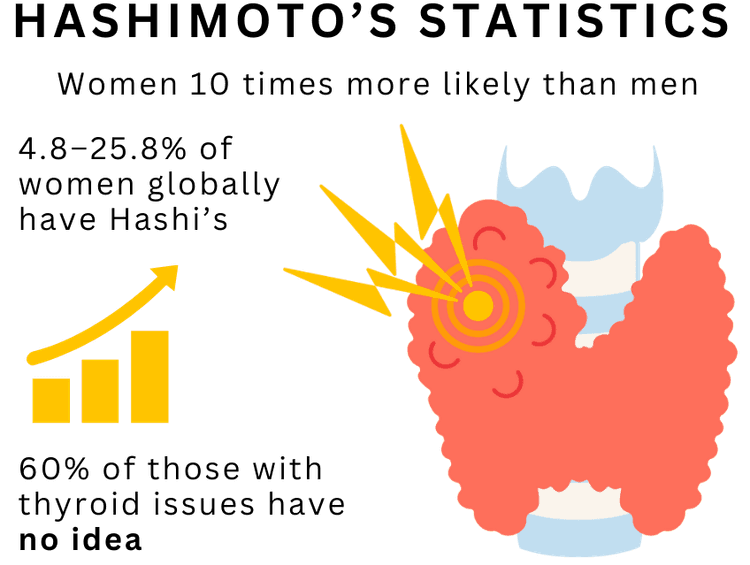
While Hashimoto's disease can affect anyone, it is most commonly seen in middle-aged women. The standard treatment involves replacing the thyroid hormones.
Hashimoto's disease is also referred to as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, and chronic autoimmune thyroiditis.
Causes
Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks thyroid cells, treating them as if they were harmful bacteria or viruses. This misguided attack damages and eventually destroys thyroid cells.
The root cause of this immune system malfunction is often overlooked, but evidence suggests it is influenced by:
- Genetic factors
- Environmental triggers such as infections, stress, or radiation exposure
- The interaction between genetic predisposition and environmental factors
We offer a free masterclass that dives deeper into these causes and will show you how understanding them can pave the way to better health.